| Availability: | |
|---|---|
| Quantity: | |
17804-35-2
95%TC, 50%WP
Benomyl
Common name: Benomyl
CAS No.:17804-35-2

Specification: 95%TC,50%WP
Molecular formula: C14H18N4O3
Structural formula:
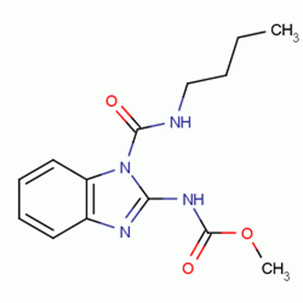

Mode of action:
Benomyl is a kind of efficient, broad-spectrum internal bactericide, and also has the function of protecting, eradicating and killing mite eggs. Its bactericidal action is the same as carbendazim, which can inhibit the formation of spindles in the cell division of bacteria, but the produced isocyanate is easy to combine with the cuticle and waxy layer of leaf and fruit epidermis, so the efficacy is often better than carbendazim. Can be used for spraying, seed dressing and soil treatment. It is mainly used to control the diseases of vegetables, fruit trees and oil crops.
Uses:
Description: A broad-spectrum foliar fungicide used to control a wide range of Ascomycetes and Fungi Imperfecti in a wide range of crops.
Example fungi controlled: Fruit spot; Powdery mildew; Scab; Post-harvest decay; Blosson end rot; Blosson blight; Brown rot; Collar rot; Phoma leaf blotch; Black spot; Corm rot; Loose smut; Sclerotina rot.
Example applications: Field crops; Nuts; Muschrooms; Ornamentals; Turf; Apples & pears; Peaches; Curcubits; Peppers; Peas; Grapes.
Benomyl
Common name: Benomyl
CAS No.:17804-35-2

Specification: 95%TC,50%WP
Molecular formula: C14H18N4O3
Structural formula:


Mode of action:
Benomyl is a kind of efficient, broad-spectrum internal bactericide, and also has the function of protecting, eradicating and killing mite eggs. Its bactericidal action is the same as carbendazim, which can inhibit the formation of spindles in the cell division of bacteria, but the produced isocyanate is easy to combine with the cuticle and waxy layer of leaf and fruit epidermis, so the efficacy is often better than carbendazim. Can be used for spraying, seed dressing and soil treatment. It is mainly used to control the diseases of vegetables, fruit trees and oil crops.
Uses:
Description: A broad-spectrum foliar fungicide used to control a wide range of Ascomycetes and Fungi Imperfecti in a wide range of crops.
Example fungi controlled: Fruit spot; Powdery mildew; Scab; Post-harvest decay; Blosson end rot; Blosson blight; Brown rot; Collar rot; Phoma leaf blotch; Black spot; Corm rot; Loose smut; Sclerotina rot.
Example applications: Field crops; Nuts; Muschrooms; Ornamentals; Turf; Apples & pears; Peaches; Curcubits; Peppers; Peas; Grapes.


